[ad_1]
The automotive landscape is on the verge of a seismic shift, and Ford’s recently unveiled patent for a modular EV platform stands as a testament to this transformative era. This ingenious design, likened to a Lego set for EVs, promises to break free from the rigid confines of traditional car manufacturing, ushering in an era of unprecedented versatility and adaptability.
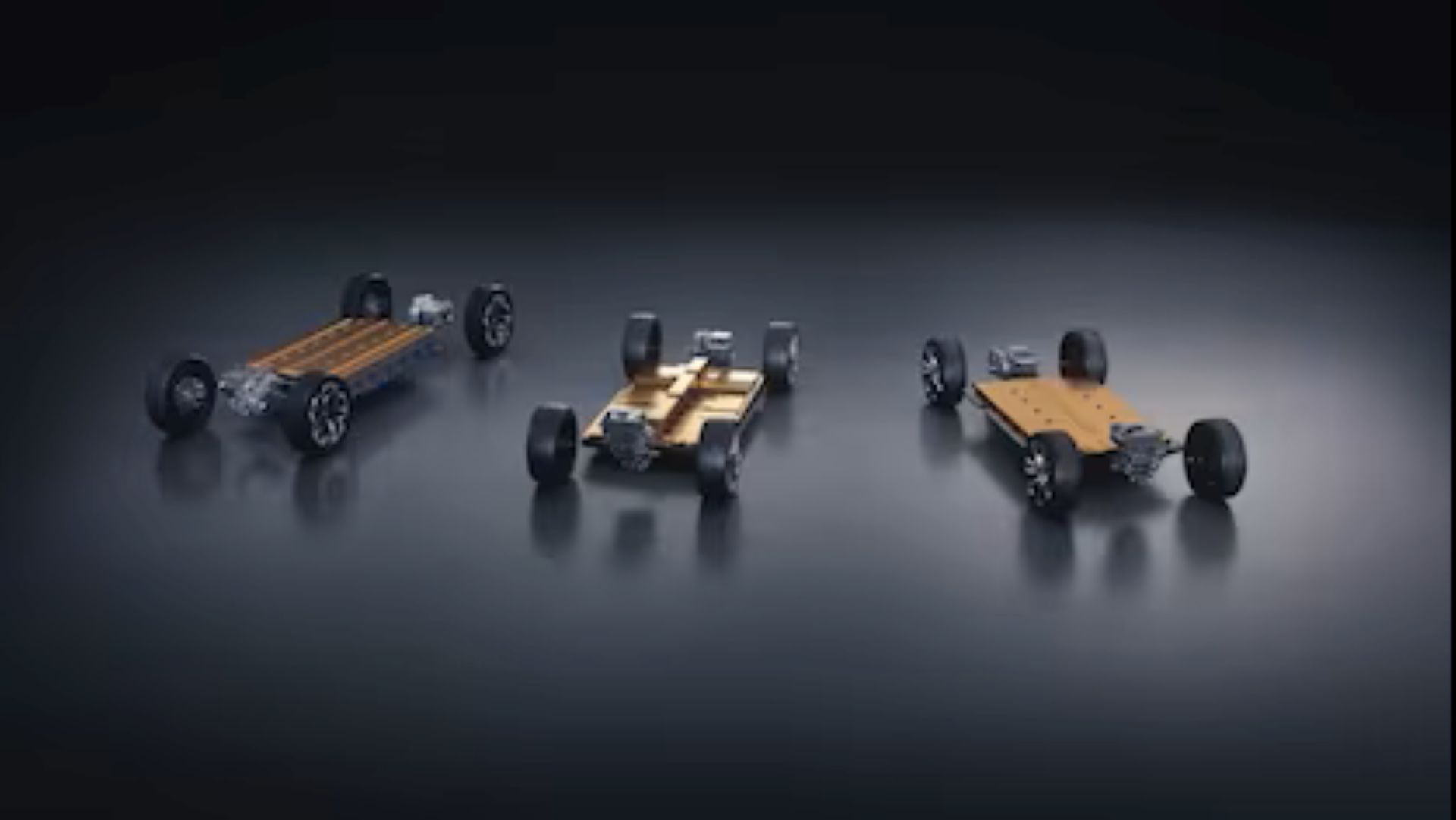
Gone are the days of dedicated platforms for each model. Ford‘s vision reimagines the assembly line, replacing it with a flexible framework capable of birthing a diverse fleet of electric vehicles, from sleek sedans to rugged SUVs and beyond. This core tenet – modularity – lies at the heart of the patent’s brilliance. Instead of sculpting bespoke platforms for each car, Ford envisions a standardized set of building blocks – interchangeable subframes, adjustable frame rails, and a plug-and-play approach to components.

Ford’s ‘Drift Mode’ For EVs Revealed In Latest Patent Filings
Ford patents an innovative ‘drift mode,’ offering controlled slides and redefining performance in the electric cars era.
In order to give you the most up-to-date and accurate information possible, the data used to compile this article was sourced from the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO), Ford, GM and other reliable sources.
Ford Attempts To Rewrite The Rulebook
Ford has unveiled a bold vision for its future EVs through a recently published patent, showcasing a highly modular platform that could revolutionize the way they’re built and offered. This innovative design promises a significant departure from traditional car manufacturing by emphasizing adaptability and versatility.
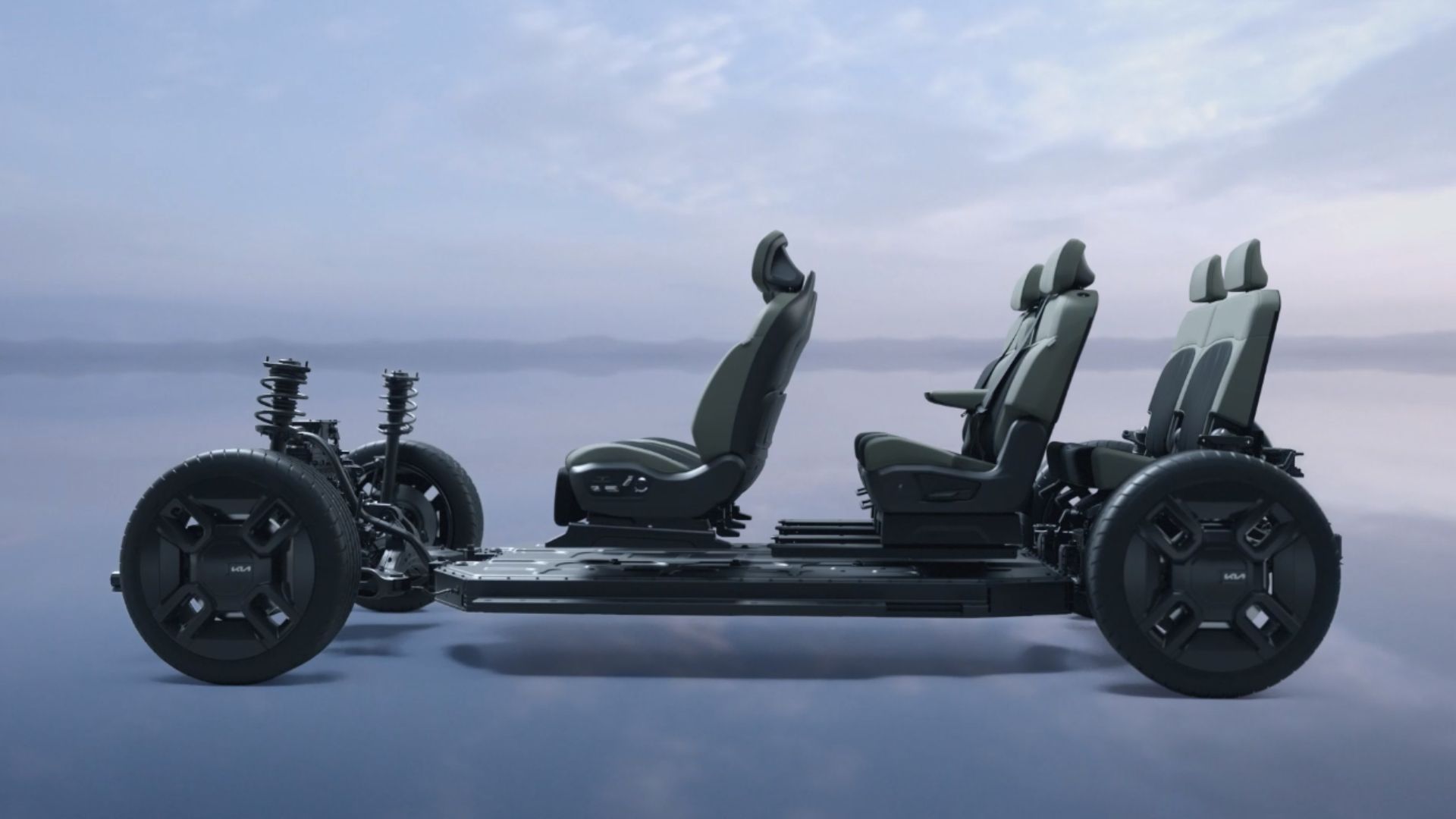
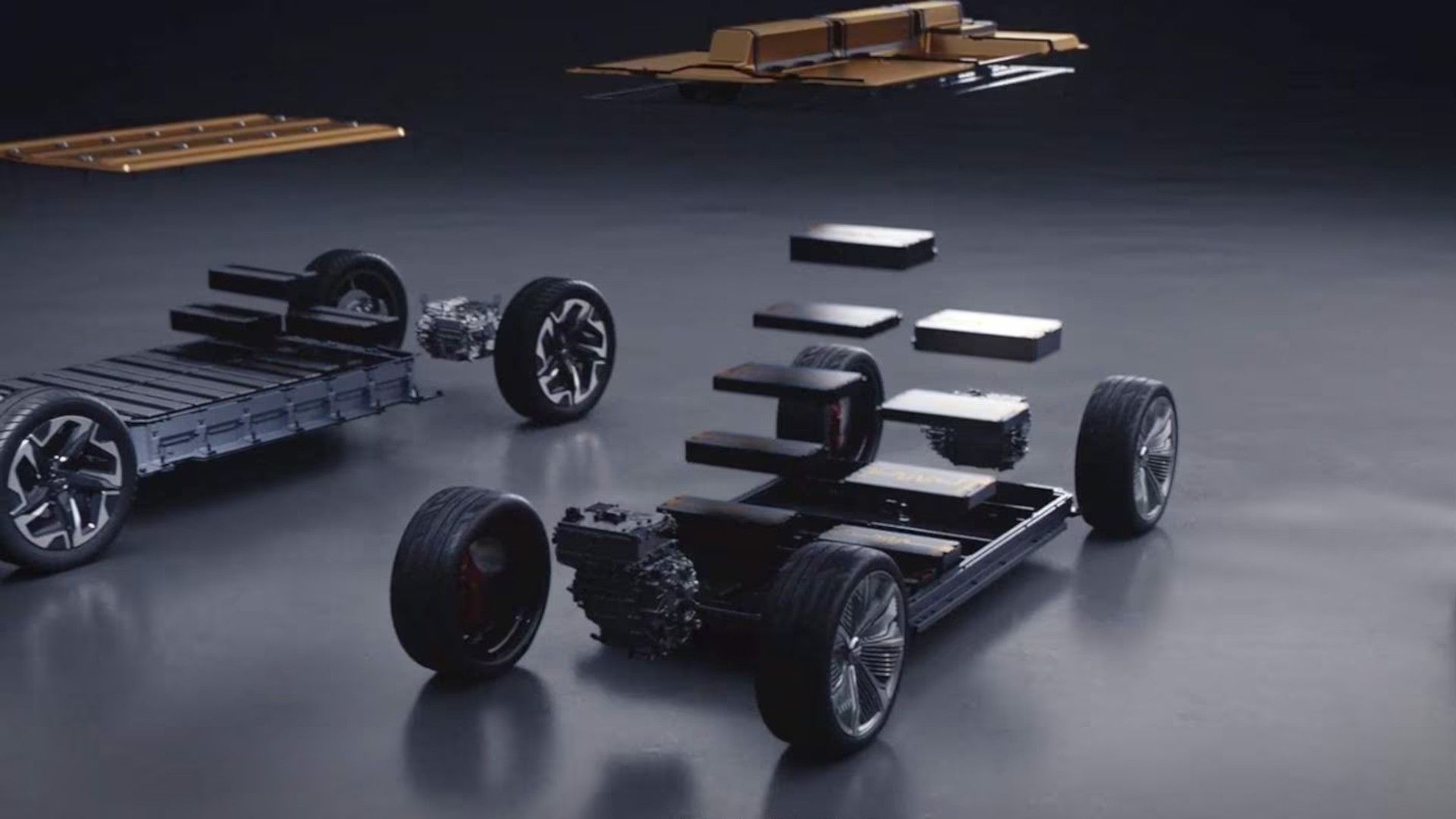
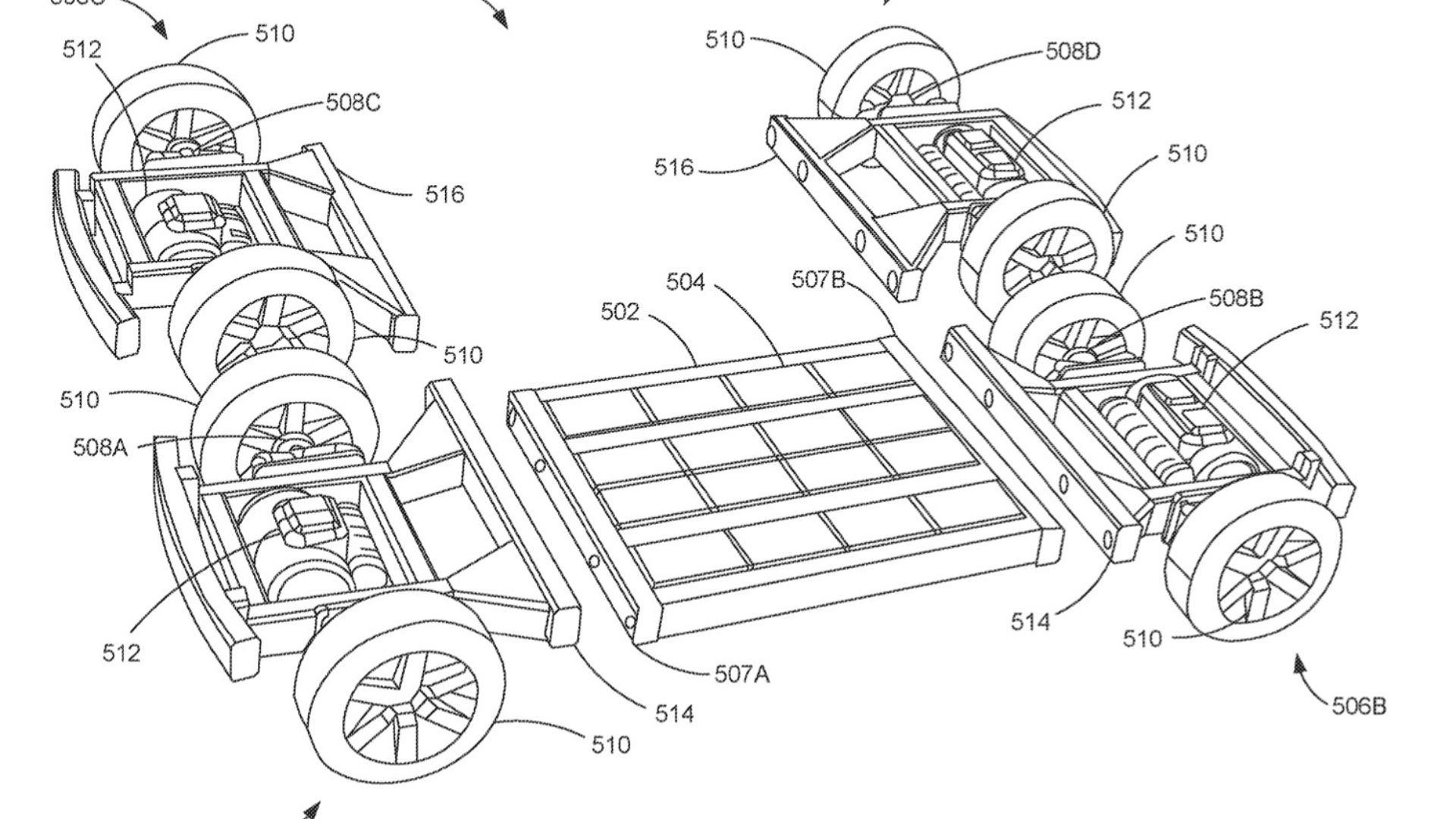
The patent, filed in 2021 and published in January 2024, describes a modular EV platform built around three standardized subframes: a central one housing the battery and two others encompassing suspension, steering, and propulsion systems at the front and rear. These subframes can be connected with adjustable frame rails and crossmembers, allowing for customization of the chassis length and accommodating diverse vehicle types, from trucks and SUVs to sports cars.
Key Features
- Extreme Versatility: The platform’s modularity shines in its ability to cater to a wide range of vehicle sizes and styles. By simply swapping bodies and adjusting the chassis length, Ford envisions creating everything from compact cars to full-size pickups.
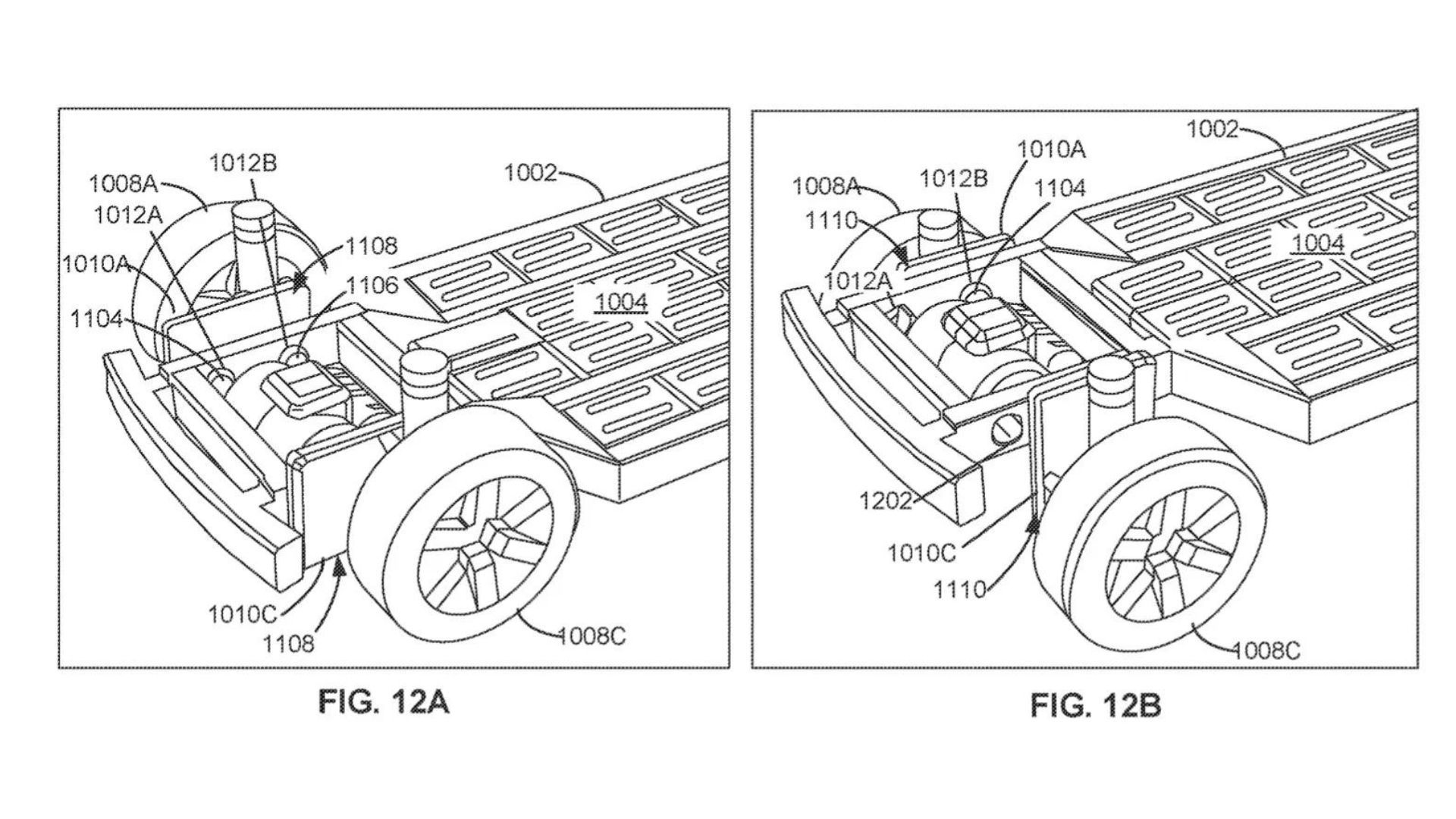
- Interchangeable Performance: The patent hints at performance packages with different motors, potentially swappable thanks to universal mounting hardware. This opens the door for personalized driving experiences without requiring extensive production adjustments.
- Ground Clearance Flexibility: The front and rear subframes can be inverted, altering ground clearance to suit specific vehicle needs. This caters to the demands of both off-road adventurers and sleek sports car enthusiasts.
- Production Efficiency: The modular approach promises significant cost savings by streamlining production and reducing the need for dedicated platforms for different models. Standardized parts and a simplified assembly process could translate to increased profitability and quicker time-to-market.
Legos For EVs
Imagine a Lego set, but one specifically designed for building electric vehicles. Each piece, from the battery pack to the suspension, is standardized and interchangeable. This is the essence of a modular EV platform. Instead of crafting a bespoke platform for each new model, automakers can mix and match pre-designed modules to create a diverse range of EVs. Think sedans, SUVs, pickup trucks, and even commercial vehicles – all built upon the same adaptable foundation.
1:14


TopSpeed’s Exclusive Rendering Reveals What The Ford Mustang EV Could Look Like
The iconic Ford Mustang is reimagined in a sleek and aerodynamic silhouette that captures its essence while embracing the future.
Ford’s Modular EV Platform vs. GM’s Ultium
Both Ford and GM, titans of the American automotive industry, are diving headfirst into the electric vehicle (EV) revolution. Each has its own approach to platform design, with Ford’s newly patented modular platform and GM’s established Ultium architecture vying for dominance. While they share some similarities, key differences set them apart.
Modular Mastermind vs. Battery Backbone
Ford’s modular platform leans heavily on flexibility. Imagine a Lego set for cars, where a central subframe with adjustable rails accommodates diverse vehicle sizes. Front and rear subframes housing motors, suspension, and wheels can be bolted on, and bodies simply placed on top. This skateboard approach allows for a wide range of models, from sporty coupes to burly pickups, all sharing the same core platform.
GM’s Ultium, on the other hand, revolves around the battery pack. It serves as the structural backbone, with modules stacked and integrated into the chassis. While offering scalability for different vehicles, Ultium focuses on optimizing battery packaging and performance.
Swapping Power And Performance
Ford’s modularity extends beyond physical dimensions. The patent hints at performance packages with swappable motors, potentially offering buyers various power levels without major production tweaks. This opens doors for personalized driving experiences within the same vehicle footprint.
Ultium, while not explicitly mentioning motor swapping, emphasizes efficient battery utilization. Its cell-to-pack design promises improved range and charging times, prioritizing overall EV performance over modularity in powertrain options.
Production Puzzle
Both platforms offer potential cost savings. Modular designs like Ford’s can streamline production by leveraging shared components across diverse models. Ultium’s focus on battery integration aims to optimize manufacturing processes and reduce complexity.
However, these benefits come with challenges. Ford’s modularity would require significant upfront investment to adapt factories and supply chains. Ultium’s tight battery integration might limit flexibility in future platform iterations.

Everything We Know About GM’s Ultium Battery Technology
GM’s bold ambition to eclipse Tesla by 2025 is fueled by its ultra-flexible Ultium battery technology. And it certainly has the potential to do so.
Benefits Of Ford’s Patent Modular Platform
Ford’s newly patented modular platform for electric vehicles (EVs) offers a range of potential benefits, from increased production flexibility and cost savings to improved vehicle customization and performance.
Reduced Production Costs
- Standardized components: By using a standardized set of subframes and frame rails, Ford can streamline production and reduce the need for specialized parts for each model. This can lead to significant cost savings in manufacturing and inventory management.
- Scalability: The modular platform can be easily adapted to different vehicle sizes and types, from compact cars to SUVs and trucks. This allows Ford to leverage the same platform for a wider range of vehicles, spreading development costs across a larger product portfolio.
- Flexible production: The modular design allows for greater flexibility in production lines, as different body styles can be assembled on top of the same basic chassis. This can enable Ford to adjust production volumes more easily based on market demand.
Enhanced Customization
- Interchangeable performance packages: The patent suggests that motors and control equipment could be easily swapped thanks to universal mounting hardware. This would allow Ford to offer buyers a wider range of performance options without requiring significant changes to the platform itself.
- Body swapping: The concept of a “skateboard” chassis with a separate body potentially enables body swapping, allowing owners to customize their vehicles or easily switch between different body styles.
Other Benefits
- Improved efficiency: The skateboard chassis design helps to optimize weight distribution and packaging, potentially leading to improved efficiency and range for EVs.
- Sustainability: The use of standardized components and reduced material waste contributes to a more sustainable manufacturing process.
It’s important to note that Ford has not yet confirmed whether it will put this modular platform into production. However, the potential benefits are significant, and it’s likely that Ford will continue to explore this concept as it develops its next generation of EVs.
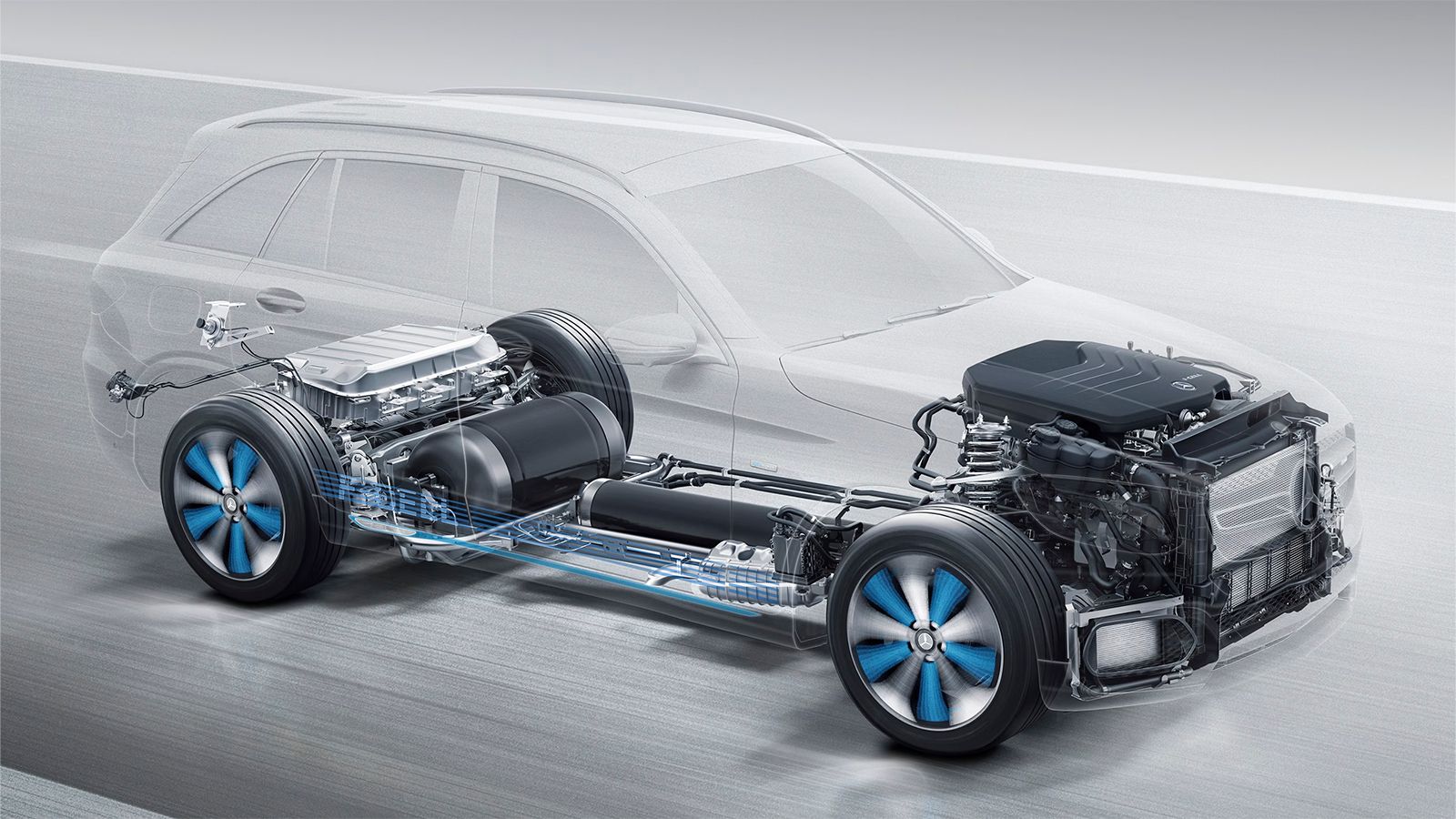

Why Infusing Hydrogen Fuel Cell System Within An EV Skateboard Platform Is A Big Breakthrough
A proposed hydrogen fuel cell system could revolutionize FCEVs just as they’re taking off, and here’s all you need to know about it.
Challenges Ahead For Ford And It’s Modular Platform
While Ford’s patent for a highly modular EV platform presents intriguing possibilities for production efficiency and vehicle customization, several significant challenges lie ahead before it could become a reality.
- Upfront Investment: Implementing such a radical departure from traditional manufacturing would require a massive upfront investment to adapt Ford’s factories and supply chain. Revamping production lines, training personnel, and potentially developing new manufacturing processes would be a costly endeavor.
- Production Complexity: Despite its modularity, assembling vehicles from pre-fabricated subframes and bodies may introduce new complexities. Coordinating the production and delivery of these components across different suppliers and ensuring seamless integration at the assembly plant could be a logistical challenge.
- Supplier Integration: Successfully implementing this platform hinges on close collaboration with suppliers. They would need to adapt their production processes to Ford’s modular specifications and potentially develop new components compatible with the platform’s flexibility.
- Uncertain Market Acceptance: While modularity offers cost savings and customization options, it remains to be seen if consumers would embrace vehicles built from interchangeable parts. Concerns about long-term durability and potential quality inconsistencies could deter buyers.
- Patent vs. Production: It’s important to remember that filing a patent doesn’t guarantee its implementation in production vehicles. Automakers often patent technologies they ultimately don’t use. Only time will tell if Ford commits to bringing this ambitious platform to market.
In conclusion, while Ford’s modular EV platform patent presents an innovative approach with potential benefits, significant challenges must be overcome before it transitions from concept to reality. The success of this platform will depend on Ford’s ability to address these challenges and navigate the uncertainties of market acceptance and production feasibility.
[ad_2]
Source link